1022. 从根到叶的二进制数之和 #
Difficulty: 简单
给出一棵二叉树,其上每个结点的值都是 0 或 1 。每一条从根到叶的路径都代表一个从最高有效位开始的二进制数。例如,如果路径为 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1,那么它表示二进制数 01101,也就是 13 。
对树上的每一片叶子,我们都要找出从根到该叶子的路径所表示的数字。
返回这些数字之和。题目数据保证答案是一个 32 位 整数。
示例 1:
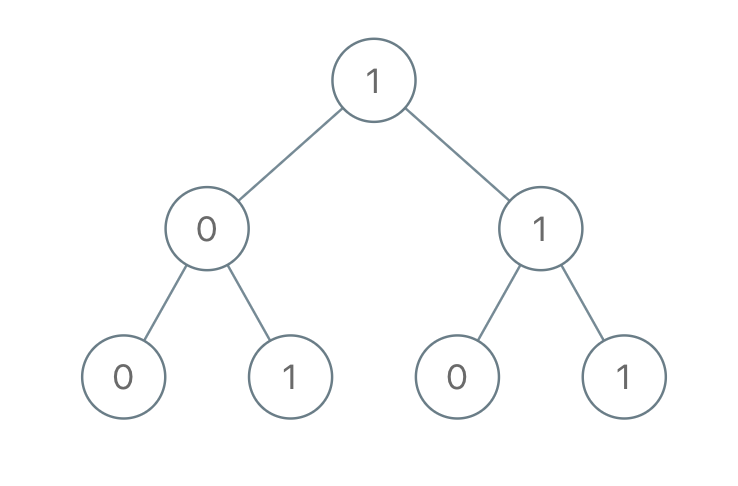
输入:root = [1,0,1,0,1,0,1]
输出:22
解释:(100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
示例 2:
输入:root = [0]
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
示例 4:
输入:root = [1,1]
输出:3
提示:
- 树中的结点数介于
1和1000之间。 Node.val为0或1。
题解 #
题解一:DFS(深度优先搜索) #
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int result = 0;
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
helper(root, 0);
return result;
}
private void helper(TreeNode node, int lastResult) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
int temp = (lastResult << 1) + node.val;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
result += temp;
return;
}
if (node.left != null) {
helper(node.left, temp);
}
if (node.right != null) {
helper(node.right, temp);
}
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度:O(N)。
-
空间复杂度:O(1)。